Lesson 1: Are Disasters Good for the Economy?

- >
- Teachers
- >
- Teacher Resources
- >
- Lesson Plans
- >
- Economics of Disasters
- >
- Lesson 1: Are Disasters Good f…
Concepts:
| human capital | economic growth | technology |
| physical capital | per capita GDP | productivity |
| Production Possibilities Frontier | real income | resources |
Content Standards:
Standard 6: When individuals, regions, and nations specialize in what they can produce at the lowest cost and then trade with others, both production and consumption increase.
Standard 13: Income for most people is determined by the market value of the productive resources they sell. What workers earn depends primarily on the market value of what they produce and how productive they are.
Standard 15: Investment in factories, machinery, new technology, and the health, education, and training of people can raise future standards of living.
Lesson Overview
Once the intense initial shock of a natural disaster has faded, the human tendency to look for the silver lining often finds consolation in believing that at least “it was good for the economy.” For example, even as it ran picture after picture of the devastation in Hurricane Katrina’s wake, USA Today cheered readers with predictions that “Economic Growth from Hurricanes Could Outweigh Costs”:
- Although natural disasters spread destruction and economic pain to a wide variety of businesses, for some, it can mean a burst of activity and revenue.
- . . . “It’s a perverse thing . . . there’s real pain,” says Steve Cochrane, director of regional economics at Economy.com, a consulting firm in West Chester, Pennsylvania. “But from an economic point of view, it is a plus.” [Hagenbaugh]
This misguided belief in the salutary effects of disaster persists centuries after it was first identified and dispatched by French economist, Frederic Bastiat. In “What Is Seen and What Is Not Seen,” Bastiat explained what has come to be called the “broken window fallacy,” emphatically denying that destruction is profitable. (See Appendix 1 below.)
While the convoys of relief supplies, the flurry of repair and rebuilding activity, and the news coverage of advertisements for $12/hr. entry-level workers may create the impression that disasters boost the economy, the economic way of thinking offers us the tools to examine the validity of that impression.
This lesson uses the concepts of scarcity and productivity, a simple graphic model (the production possibilities frontier), and historical analysis of the Black Plague and the Spanish Influenza pandemic to explain how disasters change our ability to satisfy wants and needs through production and to answer the question of whether disasters can, indeed, be “good for the economy.”
Key Points
1. Disasters increase scarcity and reduce the output of economies.
- In simplest terms, inputs are necessary for outputs; fewer inputs means fewer outputs. When a disaster damages or destroys resources – whether labor, capital, or natural resources – total production in the economy must fall.
- The production possibilities frontier (PPF) is used by economists to model “production possibilities” – the output possible in an economy making full use of its available resources. The PPF shrinks when disasters reduce the availability of the resources used to make goods and services.
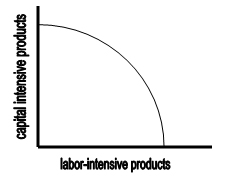
Assumptions of the PPF Model
|
- The reduction of production possibilities is shown on the graph by the retreat of the frontier. Given that the model is predicated on the full employment of resources, disaster-related destruction of resources must reduce the ability of an economy to produce goods and services.
2. Disasters affect productivity.
- Productivity is a function of the available human and physical capital, the mix of the skills and abilities of the labor force and the machines, buildings, tools, and technology available to workers.
- A key determinant of labor productivity (output per man-hour) is the amount of physical capital available to labor. The more capital available to workers, all other conditions held equal, the more productive the laborer will be. In simplest terms, workers who use tools and machines produce more with their labor than those who have none.
- Disasters change the mix of human and physical capital, but they do so in different ways. The extent of the reduction and the effect on productivity depends on how much damage or destruction is sustained by the various types of resources and how the disaster affects the capital to labor ratio in the economy.
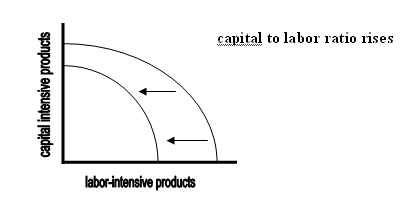
- A pandemic, for example, has a greater impact on labor-intensive production (subsistence agriculture, for example) than on capital-intensive production (information processing or industrial manufacturing), as shown by the greater shrinkage on the horizontal axis of the PPF below.
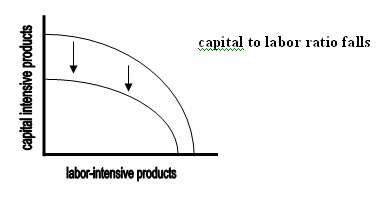
- Hurricanes and tornados (with early warning and effective evacuation of people living in the affected area) on the other hand, have a greater impact on capital-intensive production than on labor intensive production, as shown by the greater shrinkage on the vertical axis of the PPF below.
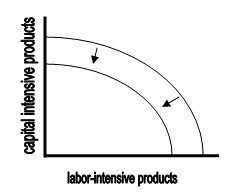
Sudden natural disasters, like massive earthquakes, floods, or volcanic eruptions that create death and destruction, shrink the production possibilities frontier on both axes.
- While these models clearly do not incorporate the complexities and the unique impacts of any real-world disaster, they do help us understand why disasters may sometimes appear to be “good for the economy.”
- A pandemic, for example, has a greater impact on labor-intensive production (subsistence agriculture, for example) than on capital-intensive production (information processing or industrial manufacturing), as shown by the greater shrinkage on the horizontal axis of the PPF below.
3. The detrimental economic effects of disasters are easier to see when the capital-to-labor ratio falls.
- Suppose a small, island nation is devastated by a huge tsunami. There was adequate warning and the population was safely evacuated, but all the buildings and machinery on the island were destroyed. The labor force (human capital) is intact, and with the help of relief organizations that set up temporary shelter, people quickly return to the island to try to put their lives back together.
- The shock to its capital (and land) resources immediately and drastically shrinks the nation’s ability to produce goods and services. While the people are ready and willing to work, they have none of the tools, machinery and technology they used before the storm hit
- One of the determinants of productivity is availability of physical capital. With less capital available to the workers, their output will fall
- Especially if the economy was very capital dependent (industrialized or heavily dependent on transportation and communication infrastructure), it will struggle to return to former levels of production until it can recover the physical capital on which its productivity depended
- Wages are a function of productivity, and as the reduced capital stock immediately lowers productivity, wages will fall.
- Additionally, the destruction of businesses will cause at least a temporary rise in unemployment, further reducing the level of worker well-being.
- The shock to its capital (and land) resources immediately and drastically shrinks the nation’s ability to produce goods and services. While the people are ready and willing to work, they have none of the tools, machinery and technology they used before the storm hit
4. Disasters may create the misleading impression of being “good for the economy” if they cause capital-to-labor ratios to rise.
- Suppose that, instead of a tsunami, the small island nation suffers an epidemic that devastates the population but leaves land and capital resources intact.
- The initial shock to the labor resource will cause the PPF to retreat. However, because land and capital still exist and are available to a smaller population, the productivity of individual workers may actually rise
- Additionally, because there is now a smaller population to support, the standard of living of the survivors on the island may actually rise
- If educated and trained workers can step into the jobs of those who perished, the economy could quickly regain its pre-disaster level of output
- Another possibility is that the large, pre-disaster population had relatively little land and capital. Perhaps there were too many farmers for the small land area, and each farmer had less land than he was able to work. After the epidemic, the surviving farmers could acquire more land, dramatically increasing the productivity, the average output per worker, of the nation.
- In either case, the island’s post-disaster output would be allocated to a smaller population, giving the impression that the disaster was “good for the economy.”
Case Study: Were the Black Plague and the Spanish Influenza “Good for the Economy”?
Two of the worst pandemics in recorded human history were the Black Plague that struck Europe in mid-14th century, and the Spanish Influenza that raged during World War I. Studies focusing on economic conditions following these pandemics are representative of occasions in which disaster seems to be good for the economy.
The Black Plague
The Black Plague spread throughout Europe, moving north from Sicily and Italy where it arrived from Asia on merchant ships. Death toll estimates from the Plague range from 25-33% of total European population. (Please see the entry in the “Catalog of Disasters” addendum to the Introduction for an overview of the characteristics and reach of the Black Plague.)
- Studies of the economies of Europe after the Black Death have revealed evidence of increasing wages in agriculture and rising incomes for craftsmen, leading to the assertion that the Plague raised real per capita incomes in medieval Europe.
- Economic historian Jack Hirshleifer reports: “That per capita income of the lower classes . . . tended to rise is evidenced by innumerable reports of individuals of lower status stepping up to fill vacant places, [and] of remissions and recontracts of feudal dues.” (103
- Hirshleifer and other researchers have even been able to quantify the increases in wages. “[In eastern England] the increase due to the plague is 32 percent for the threshing of wheat, 38 percent for barley, 111 percent for oats . . .” (102
- The explanation for this phenomenon lies in the changed capital to labor ratio. As landlords competed for the reduced supply of agricultural workers, wages increased. Additionally, as workers had more land and capital to work with, they become more productive
- While there is evidence of higher wages and standards of living from particular sectors and regions, the scholarly consensus that the Black Death reduced total output is unchallenged. Questions that remain concern the source of the changes in per capita income experienced by some groups of Plague survivors
- Some economists have noted that the smaller population had a reduced demand for land, causing a fall in the rent value of agricultural land. From this, they conclude that the incomes of the propertied classes probably fell in the aftermath of the plague. (Hirshleifer, 104
- Because the plague caused total output to fall but did not change the stock of money, the same amount of money was chasing fewer goods, causing the average price of goods and services to rise in the plague’s aftermath
- Because prices as well as wages were higher, the wage increases noted above certainly overstate the change in real wages earned by surviving workers. Nevertheless, economic historians generally agree that that the net impact of the plague was higher real wages due to the rise in the capital-labor ratio.
- Clive Bell and Maureen Lewis of the Center for Global Development note mixed outcomes, making it hard to definitively measure the changes in real per capita incomes attributable to the plague: “Whole villages were depopulated, marginal land returned to scrub and pasture, the value of land plummeted, the marginal cost of agricultural production declined, and food supplies became more plentiful. The apparatus that had tied the serf to his lord’s manor was gravely weakened, and many feudal holdings were broken up due largely to the shift to more modern contractual arrangements. Surviving tenants had the choice between taking on additional leases and moving away. Those without the means to cultivate could migrate to jobs in other villages and in the towns, where labor shortages expanded employment opportunities.” (Bell, 13)
Although it is likely that some serfs enjoyed higher standards of living because of the rise in the capital-labor ratio, this finding should not distract us from our original question of whether disasters are good for the economy. Economic change always produces winners and losers, and that some survivors’ economic well-being improved after the Black Death is not surprising. The bigger picture, however, remains clear: total output fell dramatically and the Black Death was not good for European economies.
The Spanish Flu
The Spanish Influenza pandemic started in the United States and spread quickly to Europe on World War I troop ships. Its name came from headlines in Spain, where news coverage of the epidemic was not suppressed as it was in the countries fighting in WWI. Death toll estimates range from 20-40 million, exceeding the total of all combat deaths in WWI, WWII, Korea, and Vietnam. The death toll in the United States was so high that it dropped American average life expectancy by ten years! (Please see the entry in the “Catalog of Disasters” addendum to the Introduction for an overview of the characteristics and reach of the Spanish Flu.)
- A Philadelphia Federal Reserve study of the Spanish flu notes that although collecting data from the time period and separating the impacts of the pandemic from those of WWI make economic analysis difficult, the impact was clearly negative:
- The Fed study cites National Bureau of Economic Research confirming that August 1918-March 1919, the height of the epidemic, was also a downturn in the U.S. economy associated with falling production and business failure. (Kish
- Additionally, the Congressional Budget Office has estimated that if the U.S. experienced a similar pandemic today, gross domestic product (GDP) would fall by 5%. (Kish
- In determining the effects of the Spanish flu on the U.S. economy, it is important to distinguish between reports, like that of the Philadelphia Fed, that focus on the immediate impact of the disaster itself, and others that focus on the period of recovery from the disaster. For example, a 2003 analysis of the economic impact of the 1918 flu epidemic by the Center for Economic Policy Research (CEPR) concluded: “Controlling for numerous factors . . . the results indicate a . . . positive effect of the influenza epidemic on per capita income growth across states during the 1920s.” (Brainerd, 1)
- Note that this study refers to differences in the recovery process across the states. As we saw in the analysis of the Black Plague, the immediate effect of the pandemic was to reduce real income by reducing inputs to production. Here we see that where the decline in output was initially greatest (in those states with the biggest population losses), there was also the most vigorous recovery. But it is important to remember that these faster growth rates proceeded from lower initial income levels.
- The explanation here harks back to our PPF model and the change in capital-to-labor ratios. Although there were fewer workers after the pandemic, there was an average of more capital per worker, increasing the productivity of the surviving workers. However, remember that the frontier has still retreated, indicating less total capital and lower total output.
- We should not let these numerical results obscure the scale of the human tragedy involved – that “smaller population” may be an overly benign description of the human death toll.
Thus, the examples of the Black Death and the Spanish Flu illustrate how some survivors may actually benefit from disaster. Further examination shows us, however, that while economic benefits may accrue to some survivors, they do not negate the very real costs imposed by a pandemic – costs not only to individuals and families, but to the economy as a whole.
Sources: Brainerd, Elizabeth and Mark Siegler. “The Economic effects of the 1918 Influenza Epidemic,” CEPT Discussion Paper #3791, February, 2003, p. 1 (Abstract)]
Kish, Andrew, et al. “Influenza and the Financial Services Industry: A Case Study of the 1918 Spanish Flu,” SRC Insights, Fourth Quarter, 2006. Federal Reserve Bank of Philadelphia. http://www.philadelphiafed.org/src/srcinsights/srcinsights/q4si3_06.html (10-9-07)
Munro, John. “Before and After the Black Death: Money , Prices, and Wages in Fourteenth-Century England Dec 15, 2004 http://ideas.repec.org/p/tor/tecipa/munro-04-04.html (3-30-07)
5. The contention that disasters are “good for the economy” overlooks the cost of unrealized human potential. Human loss is poignantly obvious on the personal scale but is largely invisible on the scale of “the economy.” While such loss is hard to measure on either scale, it is nonetheless real and significant.
- Economic growth measures of well-being (GDP per capita) focus on the survivors, and do not include all of the costs – seen and unseen – that are associated with population loss.
- Although they are not captured in measures like per capita GDP, the cost of human suffering and death are clearly recognized in economic analysis. A Harvard School of Public Health study of “Epidemics and Economics” (May, 2006) acknowledges the intangible and incalculable magnitude of personal loss.
If we take the economic value of human life into account, however, it is clear that epidemics have a high cost. How high, of course, depends on the economic value one assigns to life. People who die during epidemics, along with their families, obviously lose out economically. One could, moreover, add other losses to this if one places an economic value on intangible impacts such as the lost companionship and love felt by friends and relatives of the dead.” (Bloom, 14)
- Economic analysis also recognizes the economic cost of unrealized potential – the knowledge and advances that did not happen as a result of population loss. Because these are “unseen” losses, they are hard to calculate, but they are important nonetheless.
- Noted economist Julian Simon (1932-1998), who gained notoriety by challenging the gloomy predictions of the dire effects of “overpopulation,” argued the economic advantages of population growth. In doing so, he helped to conceptualize the unseen costs of population loss that accompanies disasters in terms of the benefits we might have derived from the people-not-alive and the advances-not-made
- Simon refined the thinking of earlier economists like Robert Solow and Edward Denison whose work he summarized: “Using different methods both calculated the extent to which the growth of the physical capital and of the labor force could account for economic growth in the U.S. . . . [and] Europe. They found that even after capital and labor are allowed for, much of the economic growth cannot be explained by any factor other than improvement in technological practice. . . .” (Simon, Population Matters, 168) And technology, as Simon frequently pointed out, is the fruit of the human mind
- After an extensive historical study in which he plotted great discoveries of the past against population size, Simon concluded that, all else being equal (and this is an important qualifier), “. . . the number of improvements depends on the number of people using their heads.” (Simon, Population Matters, 169
- Note that Simon’s analysis corrects for such differences as relative poverty or wealth, levels of education, and the extent of individual freedom among economies. He does not argue that large population, in and of itself, is sufficient to foster technological improvement. (Simon, Ultimate Resource, 372-3)
- Our earlier analysis confirms the role of capital in increasing productivity and well-being. Simon’s insight was to connect the amount and quality of capital to technological know-how and then to identify the positive relationship between technological knowledge and population: the more people we have, the more knowledge, and therefore the greater productivity.
- “The source of . . . improvements in productivity is the human mind, and a human mind is seldom found apart from a human body. And because improvements – their invention and their adoption – come from people, the amount of improvement plainly depends on the number of people available to use their minds.” (Simon, Ultimate Resource 2, 372)
- Calling the human mind in a free society (an important qualifier) the “ultimate resource,” Simon helps us to see the unseen costs of the population loss that accompanies pandemic disasters:
- Noted economist Julian Simon (1932-1998), who gained notoriety by challenging the gloomy predictions of the dire effects of “overpopulation,” argued the economic advantages of population growth. In doing so, he helped to conceptualize the unseen costs of population loss that accompanies disasters in terms of the benefits we might have derived from the people-not-alive and the advances-not-made
“The connections between numbers of scientists, inventors, and ideas, and the adoption and use of new discoveries are difficult to delineate clearly. But the links needed to confirm this effect seem very obvious and strong. For example, the data show clearly that the bigger the population of a country, the greater the number of scientists and the larger the amount of scientific knowledge produced; more specifically . . . scientific output is proportional to population size, in countries at the same level of income.. . . The main contribution that additional persons make to society is the new knowledge of all kinds – scientific, organizational, and everyday knowledge . . . – that they create and leave behind them. And to repeat an earlier statement, these gains are the result not only of geniuses but of a real number of work-a-day ingenious people.” (Simon, Ultimate Resource 2, 380 & 385)
6. Finally, an even-handed investigation of whether or not disasters are good for the economy must acknowledge that while they are not good for the economy, they may, indeed, provide opportunities or benefits for individual people, businesses, or groups.
- The national voluntary content standards in economics remind us that economic change produces both losers and winners. Individuals and businesses can experience real gains as a result of disasters. Recovery and rebuilding create real demands, and providers can benefit by responding.
And the “Winners” Are. . .Hurricane Katrina:
“Executives at Marriott International said . . . [that] once basic services return to New Orleans, the company expects demand from insurance adjusters and federal relief workers. ‘From a financial perspective, it is a positive, as unfortunate as the tragedy is,’ said Robert McCarty, the company’s executive vice president.. . . It is unclear how many river barges sank in the storm or how many are gone for good, but shipping rates . . . [rose in the week following the storm] in anticipation of tighter capacity.
Barges that might have earned $200-$400 a day for a 30-day trip between New Orleans and Pittsburgh are now commanding as much as $800 – $1,000.
. . . The trucking industry has had a similar bump in demand tied to Katrina. Schneider National of Green Bay, Wis., saw its truckloads increase by 13 percent last week.” (Foss)
Chicago Fire, 1871
Economist Dendy Macaulay reported changes after the Chicago Fire of 1871 that could easily be seen as “good” results.“Housing values could also increase because of a shift in the quality of houses built. Even for a wooden house, the quality of construction could have improved on average with the fire. New houses could have better plumbing, be farther from the street, or have larger rooms, all of which . . . could be considered effects of the fire.” (Macaulay)
Macaulay also found that those who could provide room and board to construction workers in the rebuilding effort reaped a 60% increase in boarding rates. The workers themselves were drawn to Chicago by the increased wages offered to laborers as the city scrambled to rebuild. Other beneficiaries included:
- timber suppliers – and their employees – from Wisconsin, who profited from the 30% increase in the price of wooden siding;
- fire brick producers – and their employees – in Philadelphia when prices skyrocketed as result of changes in the Chicago building code;
- property owners and miners of lime-free clay (used to produce fire brick) along Lake Michigan when the price of fire clay increased 10%. (New, local sources of clay were developed in response to the skyrocketing price for Philadelphia brick.)
Sources
Foss, Brad. “Profits Among Losses.” Sept. 10, 2006 http://www.ocregister.com/ocr/sections/business/business/article_669998.php (4-10-07)]
Macaulay, Dendy. “The Chicago Fire of 1871: An Empirical Analysis” pp. 23, 28, 29 May 2005 version of paper
- While economic change always produces winners and losers, the gains of “winners” should not distract us from the greater magnitude of immediate losses and unrealized future potential.
Conclusion
We should take from this lesson the firm conviction that despite our desire to look on the bright side and despite the occasional appearance to the contrary, disasters are not good for the economy. While contemporary news coverage offers tangible evidence that disasters can produce economic opportunities and benefits for some, and while economic historians continue to argue about the standard-of-living impacts on the survivors of disasters like the Black Plague and the Spanish Influenza, we are still left with the hard economic reality that disasters impose losses on economies. The destruction of resources reduces GDP by reducing productive capacity: fewer inputs mean fewer outputs.
Economic historians have long noted, and our contemporary experience confirms, that economies tend to be remarkably resilient. The speed of rebuilding after localized disasters is often nothing short of amazing, but we certainly have no evidence that allows us to argue convincingly that a disaster-induced spurt of economic activity can boost an economy beyond where it would have been had the disaster not occurred. Post-disaster improvements, and even higher standards of living among survivors, should not blind us to the reality of the economic loss. To posit that disaster should be welcomed as an economic stimulus would lead us to the logical but ridiculous policy of trying to boost the economy of a declining city by deliberately burning it down around its residents! In simplest terms, disasters increase scarcity and thereby reduce our ability to provide for people’s wants and needs. And that is clearly not good for the economy!
Having established that disasters are indeed setbacks on the path to economic well-being, we can proceed to Lessons 2, 3, and 4 and the question of how our economic, governmental, and social institutions can best respond to those setbacks.
Appendix 1: The Broken Window Fallacy
“What Is Seen and What Is Not Seen” by Frederic Bastiat
1. The Broken WindowHave you ever been witness to the fury of that solid citizen, James Goodfellow, when his incorrigible son has happened to break a pane of glass? If you have been present at this spectacle, certainly you must also have observed that the onlookers, even if there are as many as thirty of them, seem with one accord to offer the unfortunate owner the selfsame consolation: “It’s an ill wind that blows nobody some good. Such accidents keep industry going. Everybody has to make a living. What would become of the glaziers if no one ever broke a window?”Now, this formula of condolence contains a whole theory that it is a good idea for us to expose, flagrante delicto, in this very simple case, since it is exactly the same as that which, unfortunately, underlies most of our economic institutions.Suppose that it will cost six francs to repair the damage. If you mean that the accident gives six francs’ worth of encouragement to the aforesaid industry, I agree. I do not contest it in any way; your reasoning is correct. The glazier will come, do his job, receive six francs, congratulate himself, and bless in his heart the careless child. That is what is seen.But if, by way of deduction, you conclude, as happens only too often, that it is good to break windows, that it helps to circulate money, that it results in encouraging industry in general, I am obliged to cry out: That will never do! Your theory stops at what is seen. It does not take account of what is not seen. It is not seen that, since our citizen has spent six francs for one thing, he will not be able to spend them for another. It is not seen that if he had not had a windowpane to replace, he would have replaced, for example, his worn-out shoes or added another book to his library. In brief, he would have put his six francs to some use or other for which he will not now have them.
Let us next consider industry in general. The window having been broken, the glass industry gets six francs’ worth of encouragement; that is what is seen.
If the window had not been broken, the shoe industry (or some other) would have received six francs’ worth of encouragement; that is what is not seen.
And if we were to take into consideration what is not seen, because it is a negative factor, as well as what is seen, because it is a positive factor, we should understand that there is no benefit to industry in general or to national employment as a whole, whether windows are broken or not broken.
Now let us consider James Goodfellow.
On the first hypothesis, that of the broken window, he spends six francs and has, neither more nor less than before, the enjoyment of one window.
On the second, that in which the accident did not happen, he would have spent six francs for new shoes and would have had the enjoyment of a pair of shoes as well as of a window.
Now, if James Goodfellow is part of society, we must conclude that society, considering its labors and its enjoyments, has lost the value of the broken window.
From which, by generalizing, we arrive at this unexpected conclusion: “Society loses the value of objects unnecessarily destroyed,” and at this aphorism, which will make the hair of the protectionists stand on end: “To break, to destroy, to dissipate is not to encourage national employment,” or more briefly: “Destruction is not profitable.”
Source: Frederic Bastiat, Selected Essays on Political Economy. Irvington-on-Hudson, NY: The Foundation of Economic Education, Inc., trans. Seymour Cain, ed. George B. de Huszar, 1995. Online version: Library of Economics and Liberty
Sources
(see lesson guide)

Tell Our Elected Officials to Enroll in FTE Programs, Please!
January 30, 2026 Despite last-minute negotiations late this week, President Trump and congressional leaders appear to once again be on…

Foundation for Teaching Economics Opens Student Application for Summer 2026
January 12, 2026 The Foundation for Teaching Economics is pleased to announce that applications for Summer 2026 student programs are…

Making Economics Meaningful for Students
December 19, 2025 The Fund for American Studies’ Liberty and Leadership podcast features FTE’s own Amanda Stiglbauer, a longtime member of our…
